Introduction
With the rise in both the frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks, it has become imperative for organizations to establish robust cybersecurity measures. Among these, Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) stands out as a critical component of contemporary cybersecurity defenses.
What is SIEM?
SIEM stands for Security Information and Event Management. SIEM is a software solution that is responsible for gathering, storing, and analyzing security data from different resources within an organization's IT infrastructure.
SIEM is designed to provide a consolidated perspective of security events and alerts, making it easier for security teams to detect and respond to potential threats.
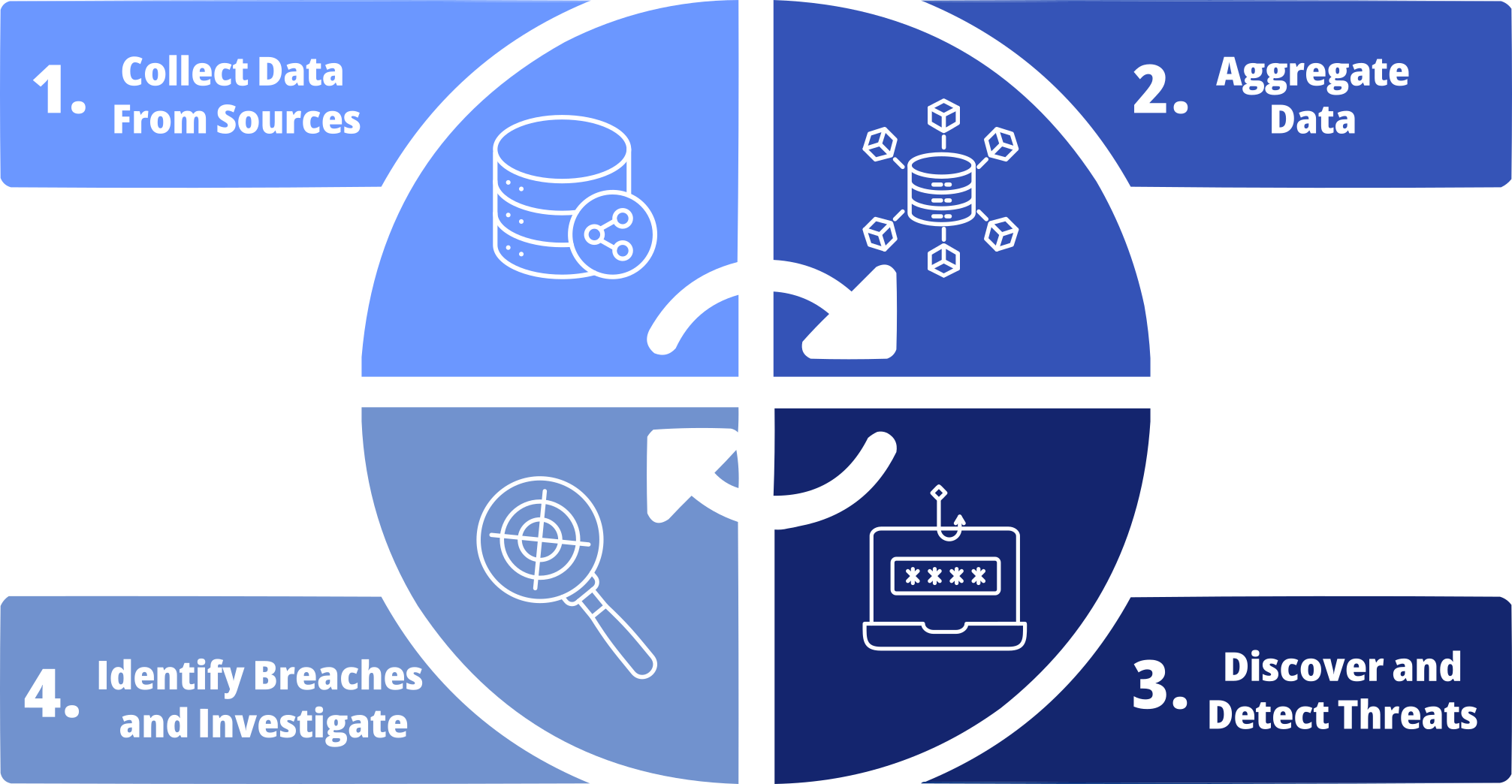
Why SIEM is Important?
Within modern cybersecurity strategies, SIEM stands as a crucial element, aiding organizations in promptly and effectively detecting and addressing security incidents. As cyber threats evolve in sophistication, they often evade conventional security measures. SIEM systems play a pivotal role by consolidating and scrutinizing data from diverse sources within an organization's network, applications, and systems. This capability allows for the real-time detection of unusual activities and potential security breaches.
Financial losses due to data breaches, theft of sensitive information, and disruption of operations can significantly impact a company's financial standing. Furthermore, the reputational harm caused by security breaches may diminish customer trust and loyalty. SIEM plays crucial role in mitigating these risks by enabling the early detection, containment, and elimination of threats, thereby reducing financial losses and safeguarding the organization's reputation and credibility.
In today's landscape of stringent data protection regulations and compliance standards, businesses must prioritize meeting their legal obligations. SIEM plays pivotal roles in ensuring organizational adherence to industry-specific regulations like Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA),the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
These systems meticulously track and document security events, generate comprehensive reports, and establish an audit trail—all essential for showcasing compliance during regulatory audits.
Overview of SIEM Architecture
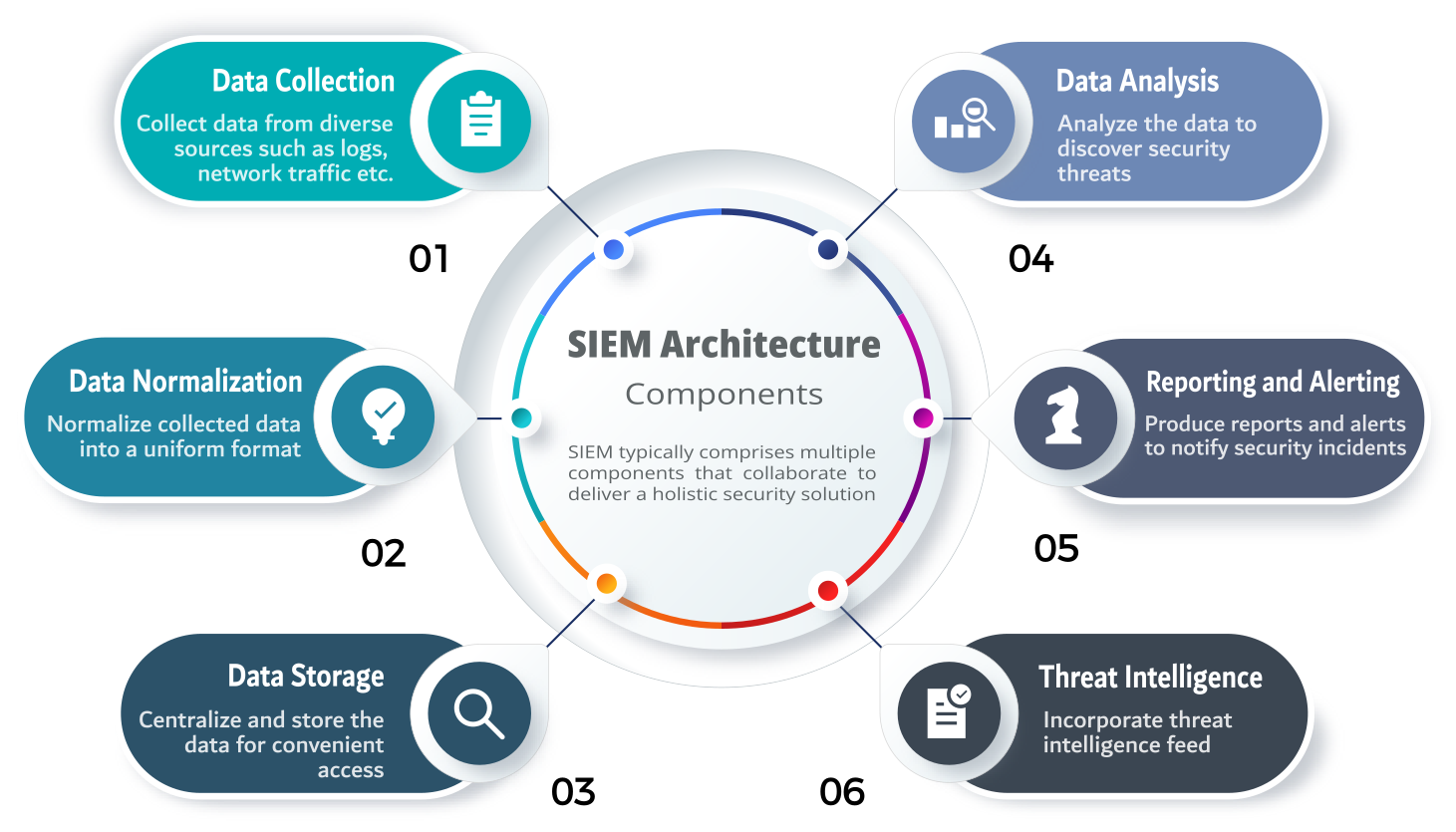
The architecture of SIEM typically comprises multiple components that collaborate to deliver a holistic security solution. Below are the main components of SIEM architecture:
- Data collection
- Data normalization
- Data storage
- Data analysis
- Reporting and alerting
- Threat intelligence
SIEM solutions gather security information from diverse sources within an organization's IT environment, encompassing network devices, servers, and applications. This information comprises logs, network traffic, and other pertinent security-related data.
The security data collected undergoes normalization to standardize it for analysis, ensuring consistency across various sources. This process entails converting data from diverse sources into a uniform format, facilitating seamless analysis by the SIEM system.
The standardized security data is centralized and stored in a repository, such as a database or data warehouse, enabling security teams to conveniently access it for analysis and reporting purposes.
The analyzed security data undergoes examination with algorithms and correlation engines to detect potential security threats. This process entails comparing the data with established patterns of behavior and rules to pinpoint any abnormal activities and potential security breaches.
Based on the analysis of collected security data, SIEM solutions produce reports and alerts. Reports offer insights into security trends, user activity, and potential threats, while alerts promptly notify security teams of potential security incidents, enabling them to take immediate action to reduce risks.
Numerous SIEM solutions incorporate threat intelligence feeds, offering details on identified threats and vulnerabilities. Utilizing this information can bolster the analysis and detection capabilities of the SIEM system.
Benefits of SIEM Technology
There are a variety of benefits to running a SIEM solution, including:
- Real time threat detection and response
- Improved visibility
- Help meet compliance
- Streamlined incidence response
- Centralized management
One of the primary benefits of SIEM solutions is their ability to detect and respond to security threats in real-time. SIEM solutions continuously monitor an organization's network, systems, and applications for potential security incidents, providing alerts to security teams when anomalies are detected. This enables security teams to swiftly investigate incidents and take appropriate action to prevent escalation. Through correlation and analysis, SIEM solutions can effectively detect and alert on threats.
SIEM solutions enhance visibility into an organization’s IT infrastructure. By aggregating logs from on-premises and cloud-based applications, servers, databases, and more, they offer deeper insights into user activities, endpoints, traffic, and other activities. This comprehensive oversight extends across the network and beyond the perimeter, especially as the organization scales. Increased visibility enables security teams to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities more effectively.
SIEM solutions assist organizations in adhering to industry regulations like HIPAA, CMMC, NIST, FFIEC, PCI DSS, and more. By monitoring compliance-related events and generating reports, SIEM solutions help organizations demonstrate compliance and avoid costly penalties and fees.
SIEM solutions can streamline incident response processes for organizations. By offering real-time alerts and automating response workflows, SIEM solutions enable organizations to address security incidents promptly and efficiently.
SIEM solutions offer centralized management of an organization's security operations. This enables security teams to handle incidents, track security-related events, and generate reports from a single platform. Centralized management also enhances collaboration among security teams, improving overall security operations.
Top SIEM Tools
Here are some of the leading players in the SIEM space:
SplunkSplunk is a highly regarded SIEM tool renowned for its robust analytics capabilities and customizable dashboards. As an excellent SIEM solution, it integrates seamlessly with nearly any network and security device, distinguishing it as a unique player in the market.
IBM QRadarQRadar provides advanced threat detection and real-time monitoring, featuring capabilities such as anomaly detection and behavioral analysis. A significant advantage is its ability to correlate, track, and identify related activities throughout a kill chain.
LogRhythmLogRhythm offers extensive log management, threat intelligence, and incident response capabilities, along with integrated analytics. It is highly regarded in the market, with many users considering it the most cost-effective and mature SIEM solution available today. However, some users report that it can struggle with handling large volumes of incoming data.
How to Select SIEM Solution
Choosing a SIEM solution is a crucial decision for any organization aiming to enhance its security posture. Here are some steps to help select the right SIEM tool:
Security requirements: The first step in selecting a SIEM solution is to determine the organization's security needs. This involves understanding the specific security capabilities required to protect assets and achieve security objectives.
Evaluate SIEM solutions: After identifying the security requirements, the next step is to evaluate SIEM solutions that can fulfill those needs. This involves researching various SIEM solutions, understanding their capabilities and limitations, and comparing them against the established security requirements.
Integration: Integration is another crucial consideration when choosing a SIEM solution. It's essential that a SIEM solution can seamlessly integrate with existing security technologies, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection systems.
Assess scalability: Scalability is another critical factor to evaluate when choosing a SIEM solution. It's important to ensure that the tool can manage the volume of logs and events produced by the organization's IT infrastructure, and that it can effectively monitor the number of devices and systems required.
Assess cost: It’s crucial to evaluate the overall capital and recurring costs of ownership, which encompass licensing fees, implementation expenses, and ongoing maintenance and support costs.
SIEM Best Practices
Implementing a SIEM system can be intricate, and organizations should adhere to several best practices ensuring the efficiency and effectiveness of their SIEM solution.
Define clear objectives:Before deploying SIEM, it's crucial to establish clear objectives outlining what you aim to achieve. This involves identifying the data sources to monitor, prioritizing threat types, and determining which metrics to track.
Plan data collection strategy:Identify which data sources are pertinent to your security objectives, and strategize efficient methods for data collection. This includes selecting appropriate data collection agents, standardizing data formats, and ensuring data quality.
Establish use cases and rules:Use cases and rules aid SIEM solutions in identifying and alerting on potential threats. Define and prioritize use cases and rules to ensure that the SIEM system effectively monitors the most critical threats.
Continuously monitor and refine:SIEM solutions require ongoing monitoring and refinement. They are not a "set-it-and-forget-it" solution. Regularly assess system performance and effectiveness, adjust use cases and rules as needed, and optimize the system to minimize false positives.
Train and equip security analysts:Effective operation and maintenance of SIEM solutions depend on skilled analysts. Provide training in SIEM best practices and ensure expertise in critical security domains such as network security, endpoint security, and incident response.
By taking these factors into account and performing a comprehensive evaluation, you can select a SIEM tool that best suits your organization’s security requirements, budget, and technical infrastructure.
Conclusion
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems are essential tools for modern cybersecurity, offering real-time threat detection, analysis, and response. By centralizing logs and alerts, SIEM enhances an organization's ability to manage security incidents and maintain compliance. Though implementation can be complex, the benefits of a well-implemented SIEM system, such as improved security posture and proactive threat management, make it a critical investment. As cyber threats evolve, organizations with strong SIEM capabilities will be better equipped to protect their data and ensure long-term resilience.
